[C#] IEnumerable VS IQueryable
IEnumerable VS IQueryable
Effective C#책을 읽다 보니.. 쿼리 구문을 사용할 경우 일반적으로 반환되는 두가지 타입에 대해서 뭐가 다른지 잘 이해하지 못해서 정리하게 되었다.
IEnumerable
제네릭이 아닌 컬렉션에서 단순하게 반복할 수 있도록 지원하는 열거자를 노출합니다.
기본적으로 ICollection인터페이스는 IEnumerable을 기반으로 확장된 인터페이스이다.
잠깐 보고 넘어가자면 모든 컬렉션의 기반 인터페이스로 구현되어 있다.
제네릭의 형태는 <>만 붙이면 된다..
1
2
3
4
public interface ICollection<T> : IEnumerable<T>, IEnumerable
{
...
}
실제로 상속받아 구현된 모습
IEnumerable인터페이스
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
namespace System.Collections
{
//
// 요약:
// Exposes an enumerator, which supports a simple iteration over a non-generic collection.
public interface IEnumerable
{
//
// 요약:
// Returns an enumerator that iterates through a collection.
//
// 반환 값:
// An System.Collections.IEnumerator object that can be used to iterate through
// the collection.
IEnumerator GetEnumerator();
}
}
요약에서도 불 수 있듯이 열거자를 가지는 메서드를 구현을 강제화 한다.
그렇다면 여기서 보이는 새로운 인터페이스 IEnumerator..?
IEnumerator
제네릭이 아닌 컬렉션을 단순하게 반복할 수 있도록 지원합니다.
- 열거자를 사용하여 컬렉션의 데이터를 읽을 수는 있지만 내부 컬렉션을 수정할 수는 없습니다. *
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
namespace System.Collections
{
//
// 요약:
// Supports a simple iteration over a non-generic collection.
public interface IEnumerator
{
//
// 요약:
// Gets the element in the collection at the current position of the enumerator.
//
// 반환 값:
// The element in the collection at the current position of the enumerator.
object Current { get; }
//
// 요약:
// Advances the enumerator to the next element of the collection.
//
// 반환 값:
// true if the enumerator was successfully advanced to the next element; false if
// the enumerator has passed the end of the collection.
//
// 예외:
// T:System.InvalidOperationException:
// The collection was modified after the enumerator was created.
bool MoveNext();
//
// 요약:
// Sets the enumerator to its initial position, which is before the first element
// in the collection.
//
// 예외:
// T:System.InvalidOperationException:
// The collection was modified after the enumerator was created.
void Reset();
}
}
즉, 설명만 보면 IEnumerable는 IEnumerator를 한번 매핑하여 반환하는 것이고 IEnumerator는 실제로 반복하기 위한 기본적인 구현 메서드들이 들어 있음을 알 수 있다.
즉, Current프로퍼티, MoveNext메서드, Reset메서드로 반복을 돌고 이에 맞는 반복 설정을 정의한 클래스에 상속 받아 구현하면 된다.
그렇다면 어떻게..?
친절하게 위의 요약과 예외까지 알려주기 때문에 쉽게 구현할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
using System;
using System.Collections;
// Simple business object.
public class Person
{
public Person(string fName, string lName)
{
this.firstName = fName;
this.lastName = lName;
}
public string firstName;
public string lastName;
}
// Collection of Person objects. This class
// implements IEnumerable so that it can be used
// with ForEach syntax.
public class People : IEnumerable
{
private Person[] _people;
public People(Person[] pArray)
{
_people = new Person[pArray.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < pArray.Length; i++)
{
_people[i] = pArray[i];
}
}
// Implementation for the GetEnumerator method.
IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator()
{
return (IEnumerator) GetEnumerator();
}
public PeopleEnum GetEnumerator()
{
return new PeopleEnum(_people);
}
}
// When you implement IEnumerable, you must also implement IEnumerator.
public class PeopleEnum : IEnumerator
{
public Person[] _people;
// Enumerators are positioned before the first element
// until the first MoveNext() call.
int position = -1;
public PeopleEnum(Person[] list)
{
_people = list;
}
public bool MoveNext()
{
position++;
return (position < _people.Length);
}
public void Reset()
{
position = -1;
}
object IEnumerator.Current
{
get
{
return Current;
}
}
public Person Current
{
get
{
try
{
return _people[position];
}
catch (IndexOutOfRangeException)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException();
}
}
}
}
class App
{
static void Main()
{
Person[] peopleArray = new Person[3]
{
new Person("John", "Smith"),
new Person("Jim", "Johnson"),
new Person("Sue", "Rabon"),
};
People peopleList = new People(peopleArray);
foreach (Person p in peopleList)
Console.WriteLine(p.firstName + " " + p.lastName);
}
}
/* This code produces output similar to the following:
*
* John Smith
* Jim Johnson
* Sue Rabon
*
*/
이런 방법으로 사용자 정의 클래스를 순회 가능하게 할 수 있다.
여기서는 크게 활용성이 없을 것 같지만 ToString overriding하여 커스텀한 내용을 추가하는 것 처럼 작동도 가능하고, 가장 중요한 LINQ의 사용이 가능해진다.
IQueryable
데이터 형식이 지정되지 않은 특정 데이터 소스에 대한 쿼리를 실행하는 기능을 제공합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
namespace System.Linq
{
//
// 요약:
// Provides functionality to evaluate queries against a specific data source wherein
// the type of the data is not specified.
public interface IQueryable : IEnumerable
{
//
// 요약:
// Gets the type of the element(s) that are returned when the expression tree associated
// with this instance of System.Linq.IQueryable is executed.
//
// 반환 값:
// A System.Type that represents the type of the element(s) that are returned when
// the expression tree associated with this object is executed.
Type ElementType { get; }
//
// 요약:
// Gets the expression tree that is associated with the instance of System.Linq.IQueryable.
//
// 반환 값:
// The System.Linq.Expressions.Expression that is associated with this instance
// of System.Linq.IQueryable.
Expression Expression { get; }
//
// 요약:
// Gets the query provider that is associated with this data source.
//
// 반환 값:
// The System.Linq.IQueryProvider that is associated with this data source.
IQueryProvider Provider { get; }
}
}
다른 점은 System.Linqnamespace에 존재하며 IEnumerable의 확장메서드라는 점이다.
인터페이스는 IQueryable 쿼리를 IEnumerable 나타내는 경우 해당 쿼리의 결과를 열거할 수 있도록 인터페이스를 상속합니다. 열거형은 개체와 연결된 식 트리를 IQueryable 실행합니다.
내부의 IQueryProvider인터페이스
IQueryProvider
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
namespace System.Linq
{
//
// 요약:
// Defines methods to create and execute queries that are described by an System.Linq.IQueryable
// object.
public interface IQueryProvider
{
//
// 요약:
// Constructs an System.Linq.IQueryable object that can evaluate the query represented
// by a specified expression tree.
//
// 매개 변수:
// expression:
// An expression tree that represents a LINQ query.
//
// 반환 값:
// An System.Linq.IQueryable that can evaluate the query represented by the specified
// expression tree.
IQueryable CreateQuery(Expression expression);
//
// 요약:
// Constructs an System.Linq.IQueryable`1 object that can evaluate the query represented
// by a specified expression tree.
//
// 매개 변수:
// expression:
// An expression tree that represents a LINQ query.
//
// 형식 매개 변수:
// TElement:
// The type of the elements of the System.Linq.IQueryable`1 that is returned.
//
// 반환 값:
// An System.Linq.IQueryable`1 that can evaluate the query represented by the specified
// expression tree.
IQueryable<TElement> CreateQuery<TElement>(Expression expression);
//
// 요약:
// Executes the query represented by a specified expression tree.
//
// 매개 변수:
// expression:
// An expression tree that represents a LINQ query.
//
// 반환 값:
// The value that results from executing the specified query.
object? Execute(Expression expression);
//
// 요약:
// Executes the strongly-typed query represented by a specified expression tree.
//
// 매개 변수:
// expression:
// An expression tree that represents a LINQ query.
//
// 형식 매개 변수:
// TResult:
// The type of the value that results from executing the query.
//
// 반환 값:
// The value that results from executing the specified query.
TResult Execute<TResult>(Expression expression);
}
}
IQueryProvider 인터페이스는 LINQ공급자를 만든다.
SQL, Entities를 만드는데 사용
마찬가지로 배열이나 컬렉션도 가능하지만 매우 비효율적인 방법..
차이점
정말 간단하게 이해하려면 IQueryable은 SQL 즉, 데이터베이스에서 로드해올 때
IEnumerable은 어플리케이션에 데이터를 사용할 때로 구분된다.
실제로 필터 로직이 실행되는 위치 또한 IEnumerable은 클라이언트에서 즉, 메모리내에서 실행되고 IQueryable은 데이터베이스에서 실행된다.
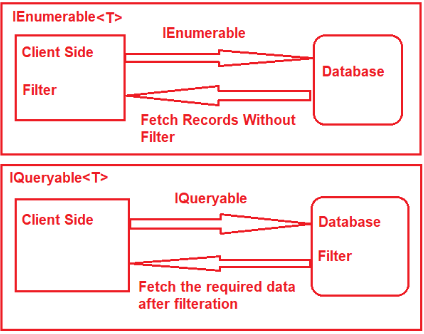
이 차이를 알아야 개발할 때 문제를 해결하거나 방지할 수 있다.
LINQ-to-Object VS LINQ-to-SQL
참고

댓글남기기